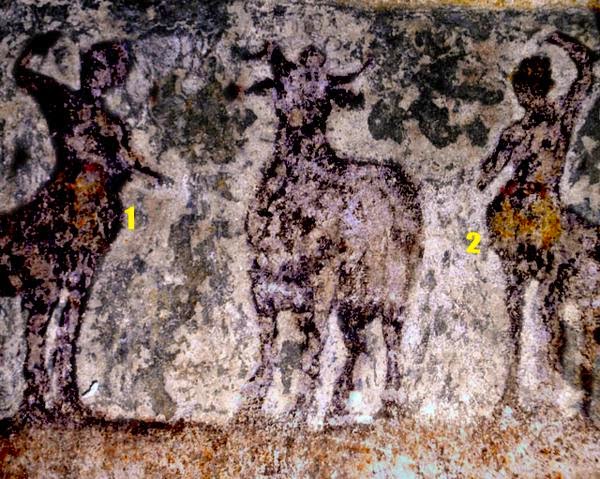 |
| Αποκαλύπτονται παραστάσεις και διακόσμηση ιωνικού κυματίου στα επιστύλια |
Το άνω μέρος του επιστυλίου φέρει διακόσμηση ιωνικού κυματίου.
 |
| Μία ελληνική Σφίγγα και ένας ελληνικός τριποδικός λέβητας.σύμβολο ελληνικό χιλιάδων χρόνων |
 |
| Από τα Κρητομυκναϊκα χρόνια ο τριποδικός λέβητας αποτελεί χαρακτηριστικό στοιχείο για τον ελληνικό πολιτισμό |
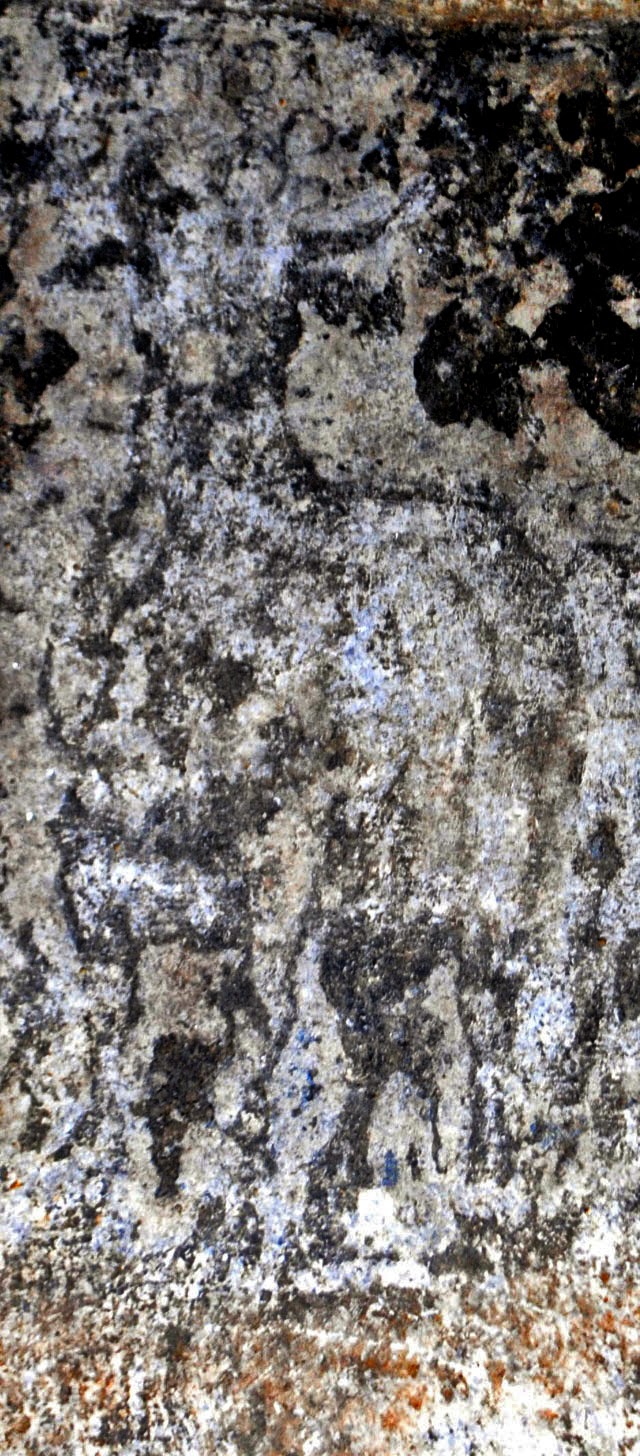
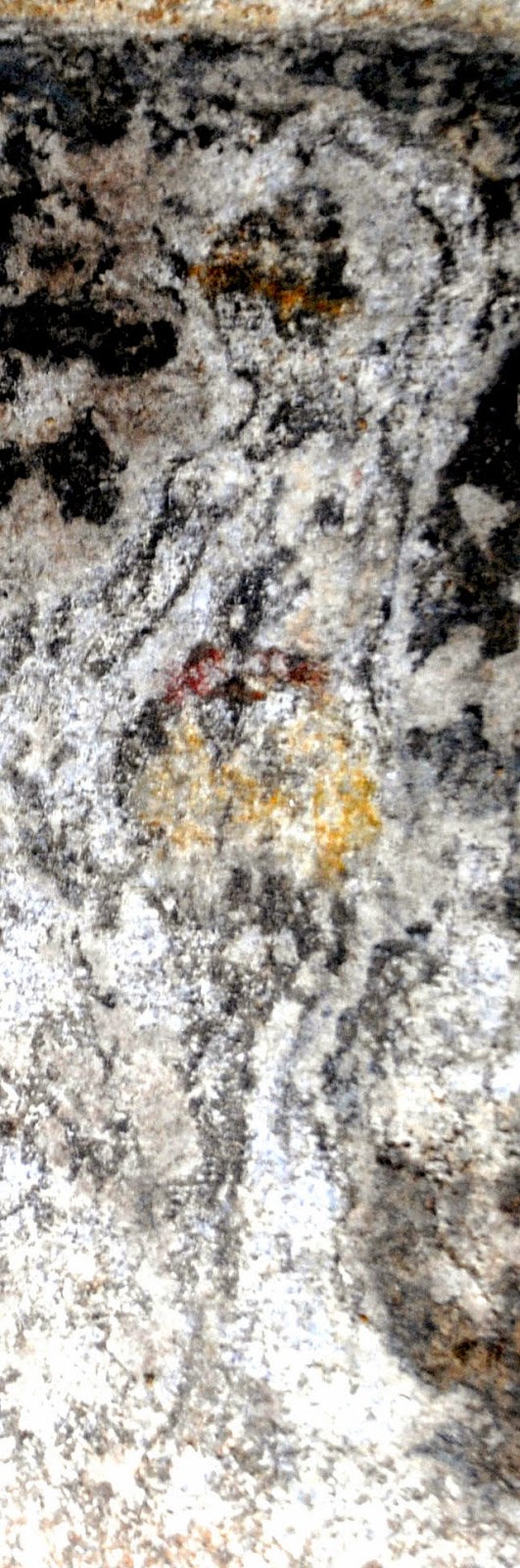
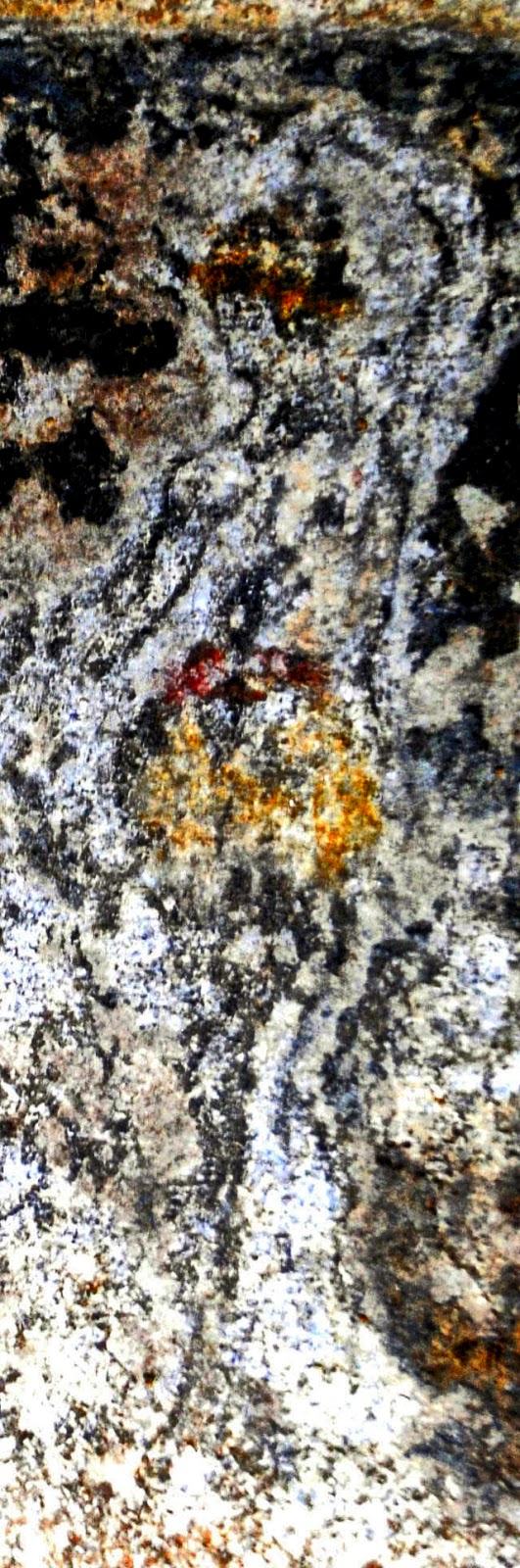
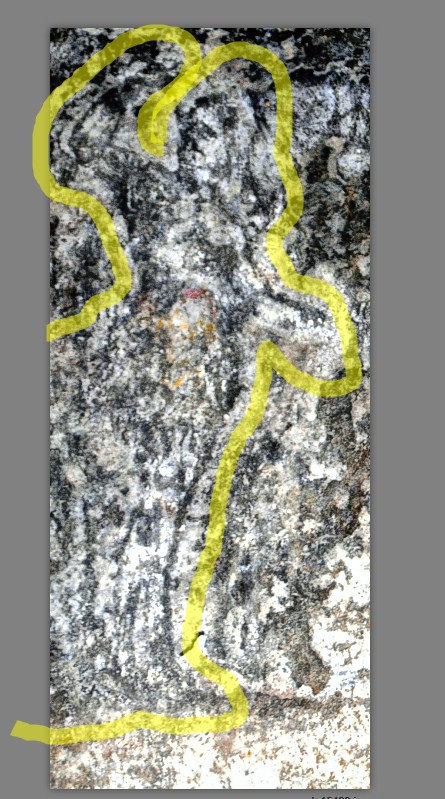
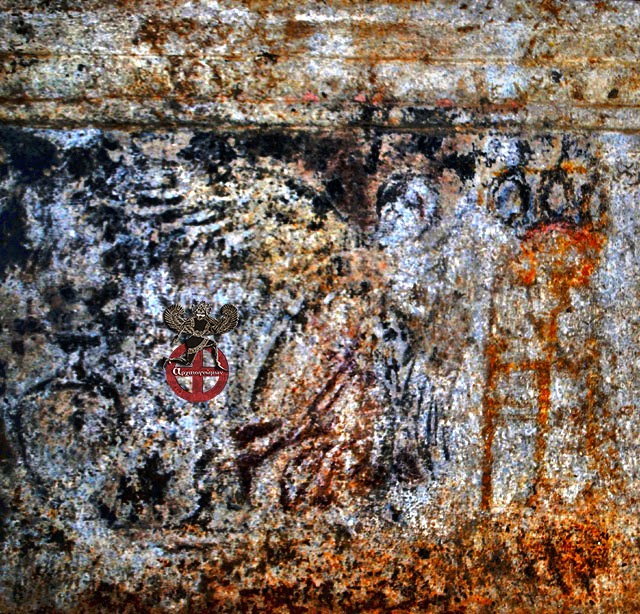
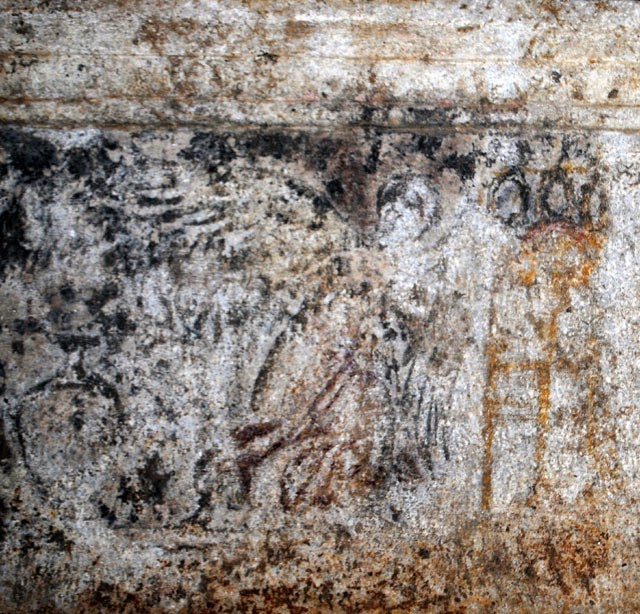
Στο ένα από τα τμήματα των “επιστυλίων”, κατά την πρώτη φάση των εργασιών συντήρησης, η οποία βρίσκεται ακόμη σε εξέλιξη, διακρίνονται στο κέντρο ζώο, πιθανόν ταύρος και εκατέρωθεν δύο μορφές, εν κινήσει, γυναικεία και ανδρική (φωτό 1,2,3,4). Δεξιά της γυναικείας και αριστερά της ανδρικής διακρίνονται υδρίες και φτερωτές μορφές. Η δεξιά φτερωτή μορφή κατευθύνεται προς ένα τριποδικό λέβητα (φωτο 5). Σε πολλά σημεία της παράστασης, όπως στο ένδυμα και στην κεφαλή της γυναικείας μορφής, στο ένδυμα της ανδρικής και της φτερωτής μορφής και στον τρίποδα, είναι εμφανή ίχνη από χρώματα κόκκινο, μπλε και ώχρα
[youtube https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=FKUac4Kdicg?rel=0]
 |
| Σύμφωνα με τον Αρριανό Ο Μ Αλέξανδρος μόλις ελευθέρωσε την Αίγυπτο από τους Πέρσες Θυσίασε στον θεό Άπι |
According to Arrian, Apis was one of the Egyptian Gods for which Alexander the Great performed a sacrifice during his seizure of the country from the Persians.[Anabasis of Alexander]
After Alexander's death, his general Ptolemy Soter made efforts to integrate Egyptian religion with that of their new Hellenic rulers. Ptolemy's policy was to find a deity that should win the reverence alike of both groups, despite the curses of the Egyptian priests against the gods of the previous foreign rulers (i.e. Set who was lauded by the Hyksos).
Alexander had attempted to use Amun for this purpose, but he was more prominent in Upper Egypt, which was not so popular with those in Lower Egypt, where the Greeks had stronger influence. Nevertheless, the Greeks had little respect for animal-headed figures, and so a Greek statue was chosen as the idol, and proclaimed as anthropomorphic equivalent of the highly popular Apis. It was named Aser-hapi (i.e. Osiris-Apis), which became Serapis, and was said to be Osiris in full, rather than just his Ka.
Η σημασία του Άπι για τούς Πτολεμαίους βασίζεται στο συμβολισμό του με την ψυχή και τον θάνατο του Μέγα Αλέξανδρου
The earliest mention of a Serapis is in the authentic death scene of Alexander, from the royal diaries (Arrian, Anabasis, VII. 26). Here, Serapis has a temple at Babylon, and is of such importance that he alone is named as being consulted on behalf of the dying king. His presence in Babylon would radically alter perceptions of the mythologies of this era, though fortunately, it has been discovered that the unconnected Babylonian god Ea was titled Serapsi, meaning king of the deep, and it is this Serapsi which is referred to in the diaries. The significance of this Serapsi in the Hellenic psyche, due to its involvement in Alexander's death, may have also contributed to the choice of Osiris-Apis as the chief Ptolemaic god.
According to Plutarch, Ptolemy stole the statue from Sinope, having been instructed in a dream by the unknown god, to bring the statue to Alexandria, where the statue was pronounced to be Serapis by two religious experts. One of the experts was one of the Eumolpidae, the ancient family from whose members the hierophant of the Eleusinian Mysteries had been chosen since before history, and the other was the scholarly Egyptian priest Manetho, which gave weight to the judgement both for the Egyptians and the Greeks.
Plutarch may not however be correct, as some Egyptologists allege that the Sinope in the tale is really the hill of Sinopeion, a name given to the site of the already existing Serapeum at Memphis. Also, according to Tacitus, Serapis (i.e. Apis explicitly identified as Osiris in full) had been the god of the village of Rhacotis, before it suddenly expanded into the great capital of Alexandria.
The statue suitably depicted a figure resembling Hades or Pluto, both being kings of the Greek underworld, and was shown enthroned with the modius, which is a basket/grain-measure, on his head, since it was a Greek symbol for the land of the dead. He also held a sceptre in his hand indicating his rulership, with Cerberus, gatekeeper of the underworld, resting at his feet, and it also had what appeared to be a serpent at its base, fitting the Egyptian symbol of rulership, the uraeus.
With his (i.e., Osiris') wife, Isis, and their son (at this point in history) Horus (in the form of Harpocrates), Serapis won an important place in the Greek world, reaching Ancient Rome, with Anubis being identified as Cerberus




















